A motherboard is a Printed Circuit Board (PCB) used to connect all of a computer’s devices and components, such as power, CPU, RAM, and peripheral devices (mouse, keyboard, etc.).
After you decide a CPU for your PC, then it’s time to look for a motherboard. There are a few things you need to consider:
- The chipset and CPU sockets of the motherboard must be compatible with the CPU you’ve chosen.
- Select the size of the motherboard (form factor). You should select a motherboard that has all of the required slots based on the features of your PC. Motherboards with ATX or microATX form factors are the most common.
- If you plan to update your RAM, SSD, or GPU in the future, you should get a motherboard with spare slots. And you’d better select the motherboard components with the latest technologies; such as PCIe 4.0 or PCIe 5.0, DDR4 or DDR5 slots.

In this article we’ll cover:
Motherboard Overview
The picture below is ASRock’s motherboard (1), supporting AMD CPU and B450 chipset. It’s consists of various components that most modern motherboards have

Major Motherboard Components
Chipset
Chipset is a set of chips for communicating between CPU, RAM, Storage and peripherals. In the past, a chipset was a collection of chips scattered throughout on the motherboard. This adds to the complexity of the system and lowers its efficiency. Until now, thanks to technical advancements, these chips have been integrated into a single chip.
Each CPU is only compatible with one or a few chipsets. It is critical to realize that you must select a motherboard with the correct chipset for the CPU you intend to buy. It’s also worth noting that chipsets are special motherboard components that are designed to work with a specific CPU family. Although motherboards are available from a variety of manufacturers, chipsets and CPUs are always produced by the same company (like Intel or AMD). Typically, the chipset’s name is also the motherboard’s identity.
For example:
Gigabyte motherboard (2) Z690 AORUS ELITE Motherboard with Intel’s Z690 chipset. This chipset supports PCIe 4.0, PCIe 4.0 and USB 3.2 Gen2.
MEG X570 ACE Motherboard is the name of the MSI motherboard(3) having AMD’s X570 chipset. This chipset supports USB 3.2 Gen2, PCIe4.0.
CPU Socket
The CPU socket is the connector that allows processors to be plugged in and connected to other components on the motherboard. As a result, you’ll need to choose a motherboard with a compatible socket type for the CPU you’ve chosen. The name of the CPU socket that corresponds to a given motherboard model is usually announced by the manufacturer.

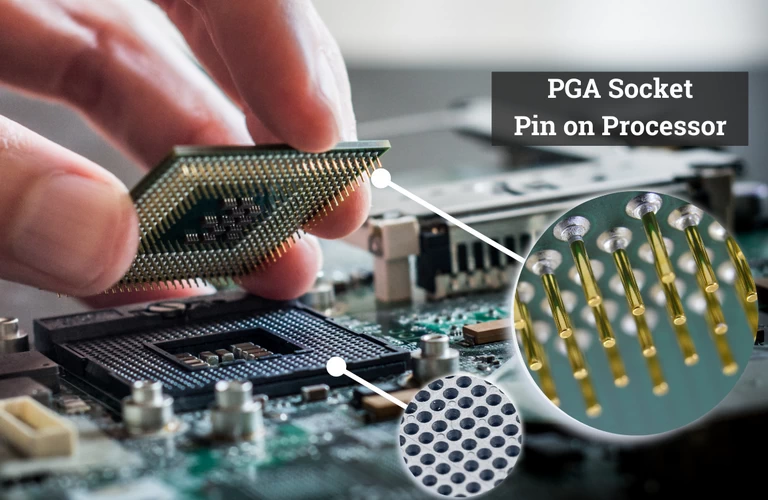
Select The Proper Socket And Chipset
The respective chipsets, sockets, and CPU series are listed in the table below. You can choose the proper motherboard by looking up the manufacturer’s specification.
| Socket Name | Launch Date | Supported Chipset | Supported CPUs |
|---|---|---|---|
| LGA2066 | 2017 | Intel X299Intel C422 | – Intel Core Processor, 7th, 9th and 10th generation- Intel Xeon Processor for server, 1st and 2nd generation |
| LGA1700 | 2021 | Intel Z690 | Intel Core Processor, 12th generation |
| LGA1200 | 2020 | Intel 400 series or 500 series chipsets | – Intel Core Processor, 10th, 11th generation- Intel Xeon Processor for server, 3rd generation |
| LGA1151 | 2015 | Intel 200 or 300 series chipsets | – Intel Core Processor, 6th, 7th, 8th, 9th generation- Intel Xeon Processor for server |
| TR4 | 2017 | AMD X399 | AMD Ryzen Threadripper Processors, 1st and 2nd Generation |
| sTRX4 | 2019 | AMD TRX40 | AMD Ryzen Threadripper Processors 3rd generation |
| AM4 | 2016 | AMD X570AMD X470AMD X370AMD B550AMD B450AMD B350AMD B520 | AMD Ryzen Processors 2nd, 3rd and 4th generation |
CPU Cooler
When the CPU is working, it generates heat. At high load, the CPU temperature can reach 185°F (85°C) or more. Therefore, cooling system is required to keep the CPU at a safe temperature so that it can function properly.
There are two primary components in a CPU cooler:
- Heatsink mounted on top of CPU: it is designed with the biggest exposed surface area to maximize heat dissipation.
- A fan cooling is used to cool the heatsink.
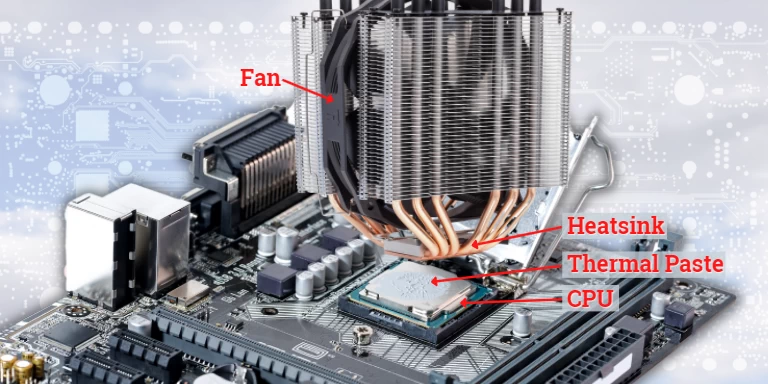
When selecting a CPU cooler, keep in mind that it must fit into the motherboard’s socket. Simultaneously, you must ensure that the whole size of the CPU cooler does not obstruct the installation of other components such as RAM, GPU, etc.
Along with the air CPU cooling system, there is also a liquid cooling system. If you use your computer to play games or run high-performance programs on a regular basis, a liquid cooling system is a great investment.
RELATED: Different Types of Liquid Cooling

PCIe Slots
PCIe (Peripheral Component Interconnect Express) is a high-speed local computer bus. It’s used to connect hardware devices such as audio cards, video cards, network cards, solid-state drives (SSDs), etc with chipset and CPU.
PCIe sizes
PCIe size is indicated by number of lane:
- PCIe x1: single lane
- PCIe x4: four lanes
- PCIe x8: eight lanes
- PCIe x16: sixteen lanes
PCIe Generations And Speed
| Generations | Introduced | ×1 Lane | ×2 Lanes | ×4 Lanes | ×8 Lanes | ×16 Lanes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PCIe 1.0 | 2003 | 0.250 GB/s | 0.500 GB/s | 1.000 GB/s | 2.000 GB/s | 4.000 GB/s |
| PCIe 2.0 | 2007 | 0.500 GB/s | 1.000 GB/s | 2.000 GB/s | 4.000 GB/s | 8.000 GB/s |
| PCIe 3.0 | 2010 | 0.985 GB/s | 1.969 GB/s | 3.938 GB/s | 7.877 GB/s | 15.754 GB/s |
| PCIe 4.0 | 2017 | 1.969 GB/s | 3.938 GB/s | 7.877 GB/s | 15.754 GB/s | 31.508 GB/s |
| PCIe 5.0 | 2019 | 3.938 GB/s | 7.877 GB/s | 15.754 GB/s | 31.508 GB/s | 63.015 GB/s |
| PCIe 6.0 | 2021 | 7.563 GB/s | 15.125 GB/s | 30.250 GB/s | 60.500 GB/s | 121.000 GB/s |
RAM Slots
RAM (Random Access Memory) is a computer’s memory with extremely fast access speed. RAM allows applications to temporarily store and access data. If your PC is running many applications at the same time or your apps have heavy load, you’ll need extra RAM. Additionally, the higher the access speed of RAM, the faster applications will run.
SDRAM (Synchronous Dynamic RAM)
SDRAM is used in most computers and laptops. “Synchronizes” means that the RAM synchronizes with the CPU clock to provide rapid and stable data access.
DDR (Double Data Rate)
DDR (Double Data Rate) is means that in the same clock frequency, DDR SDRAM can reach double the bandwidth of earlier SDRAM.
DDR4, the 4th generation DDR launched in 2016, is the most common SDRAM on modern motherboards. The 5th generation DDR (DDR5) was released in 2021 and has been supported by 12th generation Intel CPUs. DDR3, DDR2, and other older variants are no longer supported.
The following table lists some common types of SDRAM.
| DDR Name | Transfer Rate (MT/s) | Bandwidth (MB/s) |
|---|---|---|
| DDR4-1600 | 1,600 | 12,800 |
| DDR4-1866 | 1,866 | 14,933 |
| DDR4-2133 | 2,133 | 17,067 |
| DDR4-2400 | 2,400 | 19,200 |
| DDR4-2666 | 2,666 | 21,333 |
| DDR4-2933 | 2,933 | 23,467 |
| DDR4-3200 | 3,200 | 25,600 |
| DDR5-4800 | 4,800 | 38,400 |
RAM Form Factors
The Form Factor specifies the size of memory module (the RAM). There are two types of RAM sizes as follows:
- DIMM (Dual In-Line Memory Module) is RAM to mount for desktop or server. Its standard dimensions are LxH (mm) = 133.35 x 31.25.
- SO-DIMM (Small Outline DIMM) is a small-sized RAM for laptops. Its standard size is LxH (mm) = 69.6 x 30.
ECC (Error Correcting Code )
ECC RAM is a type of memory that has the function of self-detecting and correcting data errors. This type of RAM is used in computers where the applications are not allowed to have errors.
What Type Of RAM For Your Motherboard?
The selection of RAM can seem confusing because it has so much jargon. Don’t worry about it, you have two things to keep in mind:
- SDRAM in different generations cannot be interchanged. For example DDR3 cannot fit into DDR4 slots and vice versa.
- Please check your motherboard’s specifications to find what type of DDR SDRAM it supports.
- Always use RAM kits of the same brand to ensure optimal performance.
RELATED: Can You Mix RAM Brands?
BIOS or UEFI?
BIOS (Basic Input/Output System) is a low-level program (also known as firmware) that is used for the startup process of the computer. Firmware is stored in the non-volatile memory of the BIOS chip.
When the computer is turned on, the BIOS firmware is launched. It will check the hardware devices are in good working condition, and if they are, it will load the operating system from the storage device into RAM. Then all tasks on the computer will be handled by the operating system.
UEFI (Unified Extensible Firmware Interface) is the successor of BIOS. It intended to address some technical limitations of BIOS as below:
- Drives support: UEFI supports larger storage devices, up to 9 zettabytes, while BIOS can only support up to 2.2 terabytes.
- Security: UEFI provides security features. It prevents the computer from starting malicious applications.
- Running mode: UEFI could run in 32-bit or 64-bit mode, while BIOS only runs in 16-bit mode. So booting with UEFI will be faster.
- GUI: UEFI provides better user interface with mouse and keyboard navigation, whereas with BIOS only the keyboard can be used.
According to Intel’s announcement, BIOS will no longer be supported in all their chipset lines by 2020. In modern motherboards today, BIOS chip has been replaced by the UEFI chip. And the term “BIOS” is UEFI BIOS. Manufacturers may issue BIOS updates to support next-generation of CPUs or components.
Internal Ports
Power Supply Connectors
RELATED: Where Does PCIe Cables Go – A Guide To Powering Graphics Cards?
24-pin Motherboard Power Connector
The 24-pin power connector is the main power supply for motherboard operation.

4-pin (or 2×4-pin) CPU Power Connector
The 4-pin power connector is a 12V power supply for the CPU. In some modern motherboards designed for powerful CPUs, more power is required, it has an 8-pin power connector.

RELATED: CPU FAN vs CPU OPT Fan Headers
Storage Connector
PATA Port
PATA (Parallel ATA) port is the connection port for 3.5 inch Hard Disk Drives (HDD). The data transfers of this port is relatively low, 66/100/133 MB/s, so it is no longer used.
SATA Port
SATA (Serial ATA) port is the connection port for 2.5 inch HDD or Solid State Drive (SSD). This port is commonly used in today’s computers, replacing the PATA port. SATA has 3 generations:
- SATA 1: 150 MB/s
- SATA 2: 300 MB/s
- SATA 3: 600 MB/s.
SATA generations are compatible with each other. For example, If you have a HDD or SSD SATA 3.0 and plug it into a SATA 2.0 port, it will still run but at the speed of SATA 2.0 (300 MB/s).

mSATA Port
mSATA (Mini-SATA) port is the connection ports for SSD of laptops or other devices that require a solid-state drive in a small footprint. Communication speed of mSATA is limited by the SATA 3.0, which is 600 MB/s.
M.2 Port
This port is used to connect M.2 SSDs. M.2 was formerly known as Next Generation Form Factor (NGFF). M.2 SSD supports both interfaces, SATA (called M.2 SATA SSD) and PCIe (called M.2 NVMe SSDs). M.2 SATA is limited by SATA 3 speed to a maximum of 600 MB/s. While M.2 NVMe can support up to 7000 MB/s when using PCIe 3.0 x4 lanes interface.
To prevent inserting the card into an incompatible socket, M.2 card is arranged with a notch on it, called a lock. M.2 SSDs commonly use B key, M key or B + M key.

If M.2 socket on motherboard support for SATA or PCIe ×2 lanes, it is referred to as “Socket 2”, while support for PCIe ×4 lanes then it’s referred to as “Socket 3”.

External Ports
On the motherboard there are some important external connection ports as follows:
PS/2 Port
Support to connect the old generation keyboard and mouse.
USB Type A
USB Type A has supported some versions as follows:
- USB 1.0 was released in January 1996 and its full speed is 1.5 MB/s.
- USB 2.0 was released in April 2000. It supports a data rate of 60 MB/s.
- USB 3.0 was released in November 2008 with a data rate of 400 MB/s.
- USB 3.1 released in July 2013 and it has two variants. USB 3.1 Gen 1 with the data rate of 500 MB/s. And USB 3.1 Gen2 supports the data rate of 1.21 GB/s.
USB Type-C:
USB Type-C is a reversible connector. The most commonly used USB type C is USB 3.1.
HDMI/DisplayPort/DVI:
This port allows you to display high-definition video and audio to a large screen.
LAN Port
LAN port (or Ethernet Port) is the port for wired computer networking. Most modern motherboards support ethernet speed at 100 Mbps and 1000 Mbps.
Audio Port
In addition to the standard audio in/out port, some modern motherboards include an optical port for connecting to a high-end audio system.
Front Panel Header
The front panel of a PC case always comes with power switch, reset button, LED indicator for power and disk drive activity (read or write). For them to work, they must be connected to the motherboard via the front panel header.
Each motherboard manufacturer has its own name for these headers. As a result, you must consult the user manual to determine the proper installation location and follow the manufacturer’s instructions.
RELATED: How To Connect Your Motherboard’s Front Panel Connectors
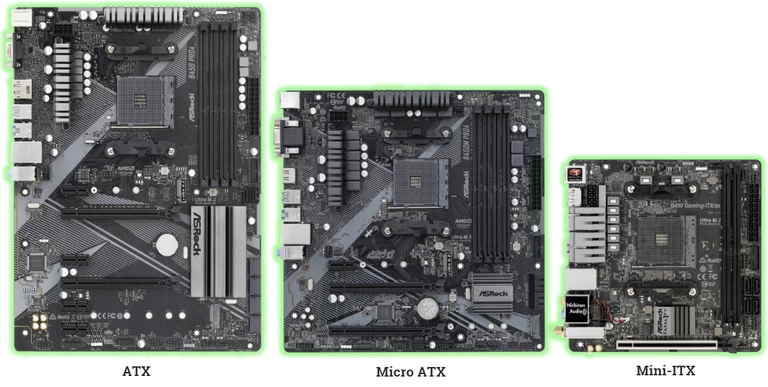
Motherboard Form Factor
The form factor is the size of the motherboard. The larger the motherboard size, the greater the number of slots that can be arranged. Then the motherboard can connect more components with a wider variety. The form factor of motherboards has been standardized and comes in four common types:
- ATX motherboard is one of the most commonly used motherboards today. The size of this motherboard is 304.8 x 243.8mm (12″ × 9.6″)
- EATX motherboard: This is an expanded version of ATX that is much larger than the standard ATX version, 304.8 × 330mm (12″ × 13″). EATX is often used for servers or gaming computers. ATX and EATX motherboards are usually arranged with up to 7 PCIe slots.
- microATX motherboard: has a smaller size than ATX but is still relatively full-featured for basic users. The size of microATX is 243.8 x 243.8mm (9.6″ × 9.6″), with up to 4 PCIe slots.
- Mini-ITX motherboard: Designed based on the ATX standard but smaller and more efficient. The design of the Mini-ITX is intended for applications in low-heat, low-power devices. The dimensions of Mini-ATX are 170 x 170mm (6.7″ × 6.7″), with up to 1 PCIe slot.
Summary
Motherboard is the main PCB that allows connection and communication of almost all components in the computer. Thus, it is very important to know the components on the motherboard and their functions.
There are several famous motherboard manufacturers such as Asus, ASRock, GIGABYTE and MSI. When choosing a motherboard for yourself, you should check their technical specification and User’s Manual.
- Select the motherboard that supports the CPU and chipset you have chosen. Note that each motherboard is only suitable for certain CPUs and chipsets.
- It’s critical that your motherboard supports the most recent connectivity standards, such as PCIe 4.0 or PCIe 5.0, as well as DDR4 or DDR5.
- Finally, choose the motherboard that is the proper size for your needs. The price must be reasonable in comparison to the general market and your budgetary constraints.
Hope this article helps you get a basic understanding to make decisions when building your own PC.





