In your PC, PCIe slots are used to connect the computer’s most important components to the motherboard. In other words, PCIe slots are used to plug in demanding and specialized parts within your computer devices.
Using PCIe slots gives you a wide range of peripheral configuration options to increase the flexibility and performance of your PC. So, if you are undecided about which components to use for building or upgrading your own PC, this article may be of assistance.
RELATED: Where Does PCIe Cables Go?
In this article, we’ll go over the fundamental terms, settings, device installation, and common applications that can be performed via the PCIe interface.
- What Is PCIe?
- PCIe Slots, How It Look?
- PCIe Lanes and Topology
- Slots Sizes vs Number of Lanes
- PCIe Generations
- Installation of PCIe Devices
- Uses of PCIe Slots
Keep reading to learn more about PCIe slots.
What Is PCIe?
PCIe (PCI Express) is an abbreviation for Peripheral Component Interconnect Express. PCIe acts as a standardized interface to connect the motherboard to components like graphics cards, solid state drives (SSDs), Ethernet cards, and more. It is a high-speed serial bus designed to replace the older PCI, PCIX, and AGP standards.
RELATED: Motherboard Components – A Guide To Building Your Own PC
PCIe Slots, How It Look?
An illustration of PCIe slots with different sizes, x1 and x16, is shown below. The slot sizes and the maximum number of lanes your computer can handle, are important parameters to consider for your selection of PC’s essential components such as graphics cards, storage devices (SSDs), and others.

PCIe Lanes and Topology
What is PCIe Lane?
A PCIe lane is a physical link used to transmit signals between PCIe devices and the CPU or chipset. Each PCIe lane consist of 2 pairs of wires (each pair is a differential signaling line) with one pair to receive the signal (Rx Signal) and the other one to transmit the signal (Tx Signal). PCIe lanes make up a point-to-point connection between devices.
A link between PCIe devices can include one or more lanes. The standard number of lanes can be x1, x2, x4, x8, x12, or x16.

PCIe Topology
PCIe Topology includes the following major components:
- Root Complex: The Root Complex device connects the CPU to PCIe devices (PCIe Endpoint) directly and/or via the PCIe Switch. It generates transaction requests on behalf of the CPU. The root complex can be integrated into chipset or CPU.
- PCIe Switch: PCIe switch is used to control a point-to-point serial connections between PCIe devices. This ensures that each PCIe device has a dedicated transmission path.
- PCIe Endpoint: Endpoints are PCIe devices such as graphics cards, Ethernet Cards, SSDs.
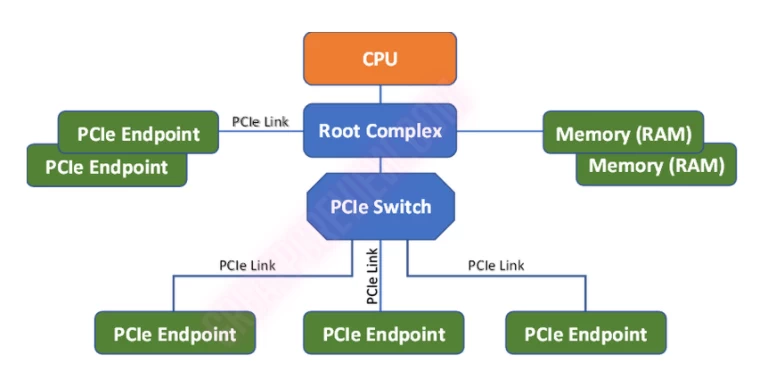
How Many PCIe Lanes In Your PC?
The number of PCIe lanes is determined by the CPU design and the chipset. As a result, the actual number of PCIe lanes will depend on which CPU and chipset your motherboard supports. You will determine the PCIe slots layout and the corresponding number of lanes based on the manufacturer’s instructions.
The following 11th generation Intel Core CPU and chipset Z590 block diagram will help you understand this issue clearly.
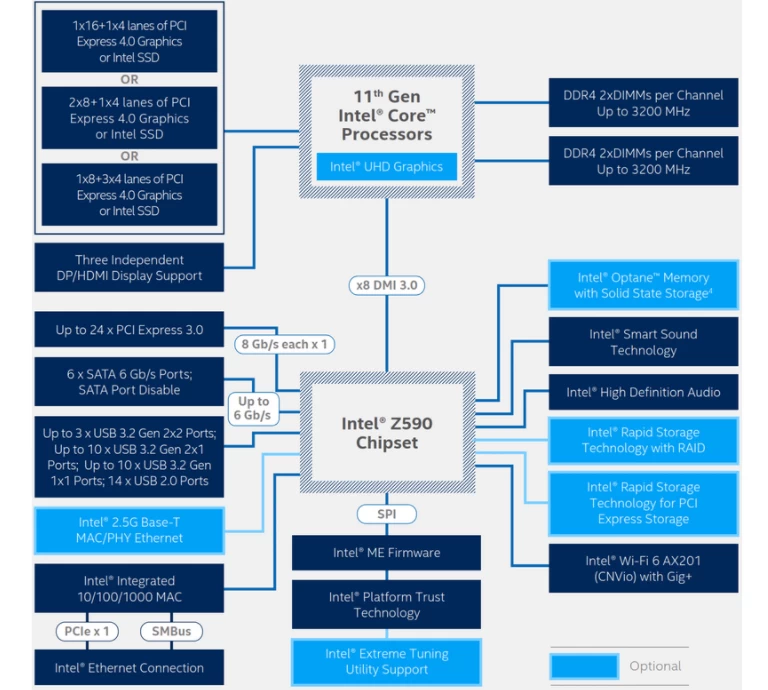
As above design of Intel, PCIe 4.0 directly linked to the CPU has 20 lanes. The motherboard manufacturer can arrange the PCIe slots in any of the following ways:
- 1×16 lanes + 1×4 lanes or
- 2×8 lanes +1×4 lanes or
- 1×8 lane + 3×4 lanes.
In addition, manufacturers can also arrange more lower bandwidth PCIe 3.0 devices connected to the chipset with 24 lanes.
To clarify, let’s take a look at a specific motherboard from the MSI manufacturer, the MPG Z590 GAMING PLUS. This motherboard uses Intel Z590 Chipset and can support 10th or 11th generation Intel Core CPUs.
Let’s see how the manufacturer actually arranges the PCIe slots.
PCIe slots connected to CPU, support up to PCIe 4.0 x20 lanes:
- PCI_E1: PCIe slot x16 lanes;
- M2_1: M.2 slot x4 lanes for NVMe SSD storage devices (This slot is also referred to as “Socket 3”).
PCIe slots connected to chipset, support up to PCIe 3.0 x14 lanes:
- PCI_E3: PCIe slot x4 lanes. This slot sharing PCIe bus with M2_2. So you can only insert either a PCIe device to the PCI_E3 slot or an storage device (NVMe SSD) to the M2_2 slot.
- PCI_E5: PCIe slot x4 lanes;
- PCI_E2: PCIe slot x1 lanes;
- PCI_E4: PCIe slot x1 lanes;
- M2_3: M.2 slot x4 lanes for NVMe SSD storage devices.
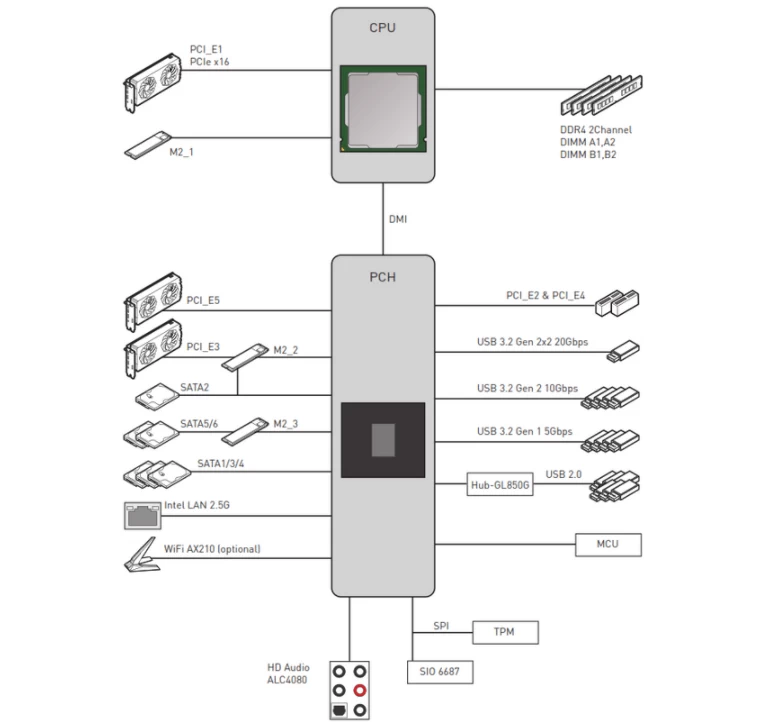
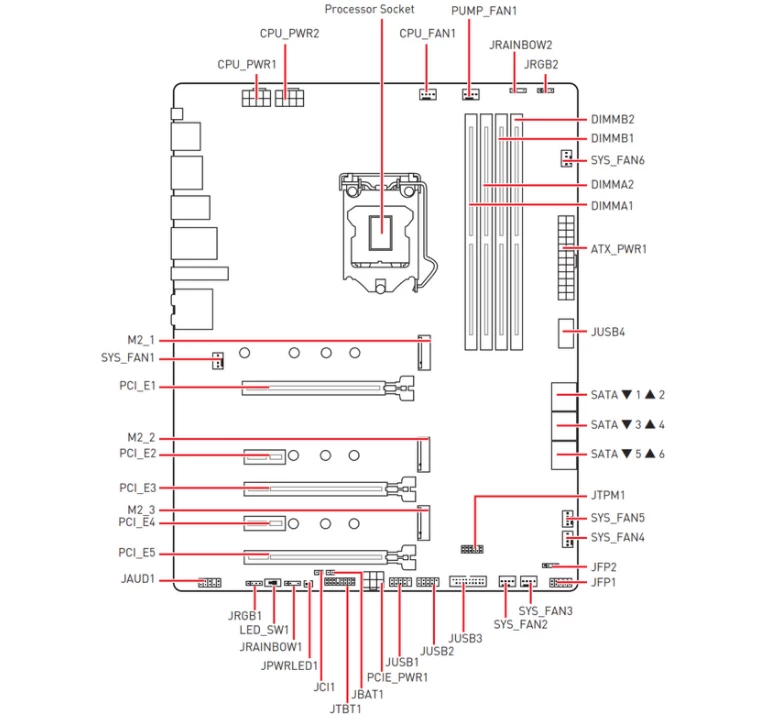
Slots Sizes vs Number of Lanes
The size of the PCIe slots will correspond to the standard number of lanes:
| Sizes | Overview |
|---|---|
| * PCIe x1: 18 pins, 25 mm long | |
| * PCIe x4: 32 pins, 39 mm long | |
| * PCIe x8: 49 pins, 56 mm long | |
| * PCIe x16: 82 pins, 89 mm long |
The specifications regarding PCIe slots sizes and lanes can be misleading. The PCI_E1 slot, like on the MSI Z390-A PRO motherboard below, has an x16 size and 16 lanes linked to the CPU. However, the PCI_E4 slot has same size (PCIe x16) but physically wiring to the Z390 chipset 4 lanes only. This means that the PCI E4 slot is x16 in size and has x4 lanes.
Therefore, to determine the PCIe’s lanes number of a slot on the motherboard you must check through the manufacturer’s specifications.

PCIe Generations
Since PCIe 1.0 was released in 2003, subsequent generations of PCIe have changed significantly in order to improve performance. The transfer rate per lane on a next-generation is frequently double that of the previous generation.
As a result, you would get significantly more data transferred each second. If you used PCIe slots and cards from the same generation, it would maximize the speed gain.
In 2021, the first PCIe 5.0 with transfer rate of 63 GB/s became available to consumers. And motherboards featuring Intel’s Z690 chipset and PCIe 5.0 support were released. GIGABITE’s AORUS and Ultra Durable series motherboards, as well as MSI’s MPG Z690 motherboards, are examples of well-known manufacturers.
It appears that AMD’s applications for PCIe 5.0 are slower than Intel’s, but we expect AMD to release a new generation of CPUs and chipsets that support PCIe 5.0 in the near future.
Remember that bandwidth capacity depends on PCIe lanes. All above bandwidth values come from PCIe x16 slots and cards. Here is a summary of the PCIe performance for various generations and its throughputs.
| Generations | Introduced | ×1 Lane | ×2 Lanes | ×4 Lanes | ×8 Lanes | ×16 Lanes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PCIe 1.0 | 2003 | 0.250 GB/s | 0.500 GB/s | 1.000 GB/s | 2.000 GB/s | 4.000 GB/s |
| PCIe 2.0 | 2007 | 0.500 GB/s | 1.000 GB/s | 2.000 GB/s | 4.000 GB/s | 8.000 GB/s |
| PCIe 3.0 | 2010 | 0.985 GB/s | 1.969 GB/s | 3.938 GB/s | 7.877 GB/s | 15.754 GB/s |
| PCIe 4.0 | 2017 | 1.969 GB/s | 3.938 GB/s | 7.877 GB/s | 15.754 GB/s | 31.508 GB/s |
| PCIe 5.0 | 2019 | 3.938 GB/s | 7.877 GB/s | 15.754 GB/s | 31.508 GB/s | 63.015 GB/s |
| PCIe 6.0 | 2021 | 7.563 GB/s | 15.125 GB/s | 30.250 GB/s | 60.500 GB/s | 121.000 GB/s |
Installation of PCIe Devices
Compatibility of Generations
PCIe is forward compatible. You can plug PCIe Gen 1.0 devices into PCIe Gen 4.0 slots. However, the bandwidth of the device will reach the speed of Gen 1.0.
PCIe, on the other hand, is backward compatible. PCIe Gen 4.0 devices can be plugged into PCIe Gen 2.0 slots. And also, the device only achieves the maximum rate of 2.0 generation.
In all cases, PCIe versions are compatible with each other. Whether forward or backward compatible, the device reaches its maximum rate in the lower PCIe generation only.
Matching Devices and Slots
Returning to the MSI Z390-A PRO motherboard example, many people may wonder: if I have a graphics card with x16 lanes, will it work if I plug it into the x4 lanes slot (PCI_E4)? And how is its performance? The answer is yes. Your graphics card will continue to work, but it will not achieve the maximum performance for which it was designed. You can see how it performs in real life by referencing the test of Gamers Nexus.
When you have an x16 lanes slot, you’ll be most efficient using 16 lanes PCIe devices in that slot. However, you can still use an x1, or x4, or x8 device on that x16 slot. This is because the PCIe lanes connect point-to-point between devices, so plugging in devices with fewer lanes has no effect on their operation and performance.
Recommendation
When installing PCIe devices, you will notice some characteristics as listed above. But here’s some suggestions:
- Purchase the most recent generation of PCIe devices that are compatible with your CPU/motherboard. If you choose a graphics card 3.0 for the MSI MPG Z690 motherboard that supporting PCIe 5.0, you will be wasting your money.
- Use the appropriate devices for the slots: If you have an x16 graphics card, using the first slot (connected to the CPU) is recommended. It is best to insert the device into the slot with the same size and number of lanes.
Uses of PCIe Slots
Most PC have extra PCIe slots these days. Depending on your motherboard, you may not be able to use all of these options. However, you might be able to implement some of these PCIe cards on your computer.
The most common applications for PCIe slots are graphics cards and storage devices. PCIe slots are also used to connect other peripherals like WiFi cards, TV Tuner cards, video capture cards, sound cards, RAID controller cards, and USB expansion cards.
Graphics Cards
Graphics cards are the most common devices that use PCIe slots. Using discrete graphics cards will significantly improve the graphics processing, especially if your PC uses it for gaming or 3D animation rendering.
There are some well-known graphics cards on the market, such as ASUS, MSI, Gigabyte, EVGA. Most of them are designed with x16 lanes PCIe. And these cards mainly use GPU chips from NVIDIA and AMD manufacturers.
The manufacturers of some motherboards may support the integration of two graphics cards at the same time. This feature is intended to improve the video card’s image rendering performance. Where each video card, along with synchronization, is in charge of half of the screen.
NVIDIA and AMD, two GPU chip manufacturers, have released generations of graphics cards with this pairing feature. That is NVIDIA’s SLI and AMD’s Crossfire technology. As a result, this simultaneous pairing will double graphic performance.
RELATED: What Is SLI? Is SLI Worth It? A Guide for Multi-GPU Technology
Storage Cards
Today’s storage devices are gradually shifting to solid-state drives (SSDs) as technology advances, and “NVMe SSD” is a term that appears frequently on online search engines.
NVMe is an abbreviation for Non-Volatile Memory Express. It is a set of standards that define how host software communicates with non-volatile memory across multiple transport media such as PCIe®, RDMA, or TCP. And when it comes to the term NVMe SSDs, we know that it is a storage device that supports PCIe connectivity.
NVMe SSDs cards do not use standard PCIe slots. Instead it uses M.2 slots.
M.2 slot for the first generation of NVMe SSDs using PCIe x2 lanes interface. And later, all modern motherboards today support PCIe x4 lanes.
In terms of Intel’s most recent design, the chipset Z690 supports PCIe 4.0 x 4 lanes for M.2 NVMe SSDs, with maximum bandwidth approaching 8GB/s.
WiFi Cards
Most modern laptops and desktops have wireless internet connectivity. However, a WiFi card could strengthen a weak signal and compensate for any router issues. Also, you can bypass your built-in system with a WiFi card.
TV Tuner Cards
TV tuner cards will let your PC receive television signals at the most basic level. Some cards will give you access to FM and AM radio signals as well. Usually, TV tuner cards are bundled with video capture cards.
Video Capture Cards
Video capture cards offer dynamic recording functionality. Many professional gamers have video capture cards to produce high-quality videos of their gameplay. Twitch streamers also use video capture cards to share a crisp image of what they play on their computer screen.
You will often find a video capture card bundled with TV tuner cards, so you have access to three entertainment options: video capture, television, and radio.
Sound Cards
If you have a damaged, aged, or low-quality sound card, you can improve the audio output of your PC with your PCIe slot. Keep in mind that you will need to deactivate your existing audio system and add a new card to enhance the sound.
Sound cards do not have high bandwidth requirements, and most work with older PCI slots without any performance degradation.
RAID Controller Cards
Those with vast storage arrays may wish to mount a RAID controller on the PCIe slot. This way, you can upgrade the storage throughout the motherboard. Many modern motherboards have some RAID functionality built-in, so you might not need this type of PCIe card.
USB Expansion Cards
If your computer does not have enough a USB port, you can get a USB expansion card to add this functionality to your PC.
Conclusion
PCIe is a standardized interface that connects the motherboard to peripheral components, such as graphics cards and storage devices. It is the industry standard with high performance, and the technological rollout has met the growing demands of modern entertainment systems.
Further, you can use your PCIe slots to connect many other devices such as TV, radio, and video capture cards. It can also expand your PC’s storage system, improve the sound quality, enhance the graphics, and increase internet speeds.
Take advantage of your PCIe slot today and maximize the performance of your PC.





