
One of the most overlooked components of a computer system is the power supply unit (PSU). Many users tend to overlook the importance of a quality PSU and instead focus on the latest graphics card or processor. However, investing in a quality power supply can improve the longevity and stability of your system.
As one of the single most important considerations when it comes to constructing a personal computer, choosing the right power supply for your rig carries incredible relevance. But before you make that all-important decision, allow us to guide you through an insightful showdown between modular vs non-modular PSUs – complete with comprehensive pros and cons so you can reach an informed decision.
Gear up! It’s time to get started on this exciting journey into your PC builds!
What is a Power Supply Unit (PSU)?
A Power Supply Unit (PSU) is an essential component of a computer system that converts the AC (alternating current) supply from a wall outlet into DC (direct current) power that is used by the computer’s internal components.
In simpler terms, a PSU is like a power transformer that takes the power from an outlet and transforms it to the right voltage and current suitable for the computer hardware to function properly. The PSU is a fundamental component in every computer system as it controls the power supply to all other computer components such as graphics cards, CPU, motherboards, hard drives, and more.
RELATED: Motherboard Components – A Guide To Building Your Own PC
What is a Modular PSU?
A modular PSU is a type of computer power supply that allows users to detach or connect cables as necessary. This design offers greater flexibility and customization compared to traditional power supplies, which have a fixed set of cables that cannot be removed.
There are two types of Modular PSU, Fully Modular and Semi-Modular. Fully Modular PSUs allow all cables to be disconnected, while Semi-Modular PSUs have some essential cables such as 24-pin motherboard power cables or 4-pin (or 2×4-pin) CPU power cables that are permanently attached. This feature makes Modular PSUs a popular choice among PC enthusiasts who value efficient cable management and a cleaner aesthetic.
Fully Modular PSU
With the fully modular PSU, you can customize your cable management to meet all of your needs. The modularity feature has gained popularity among tech enthusiasts, gamers, and computer builders. However, like any other technology, the fully modular PSU has its pros and cons.
Pros:
1. Cable Management – Fully modular PSU allows for a cleaner and more organized workspace as there are no excess cables to maneuver through. It assists in optimal airflow, which is essential for good system performance.
2. Power Efficiency – Since you only use the necessary cables, there is less electricity loss due to cables, thus increasing power efficiency. This feature makes it a preferred option for small form factor builds.
3. Future Proofing – Fully modular PSU enables users to swap out cables and has the potential for a longer lifespan. If a user wants to upgrade their build, they can easily do so by adding or replacing the cables instead of buying a new PSU.
Cons:
1. More Expensive – Modular PSU systems are more expensive than non-modular.
2. Installation Complexity – Even though modular PSU makes cable management more straightforward, it requires more setup time and effort. This demands extra attention since users need to align the right cable with the relevant connector. If installed incorrectly, it could damage the PSU or connected components.
3. Connectivity Issues – Over time, the connectors of the modular cables can weaken, become loose or corrode, resulting in connectivity issues. Moreover, if a user loses a cable or needs more than the PSU came with, additional cables have to be purchased separately.
Semi-Modular PSU
Semi-modular power supplies are a great compromise between fully modular and non-modular options. They provide the convenience of removable cables while still offering some permanently attached essential cords, eliminating many of the drawbacks associated with fully modular units. Let’s take a deeper look at their advantages and disadvantages.
Pros:
1. Cost-Effective: Semi-modular power supplies are less expensive than fully modular ones, making them a budget-friendly option for those who want a little more flexibility than a non-modular PSU.
2. Easy Installation: Semi-modular PSUs come with cables pre-attached to the unit, so you don’t have to worry about connecting everything. On the other hand, you can easily add extra cables when required.
3. Balanced Flexibility: Semi-modular power supplies provide the best of both worlds – you can retain the essential cables from the unit while still enjoying the flexibility to add more cables when needed.
4. Reduced Cable Clutter: Semi-modular power supplies significantly reduce the amount of cable clutter in your PC, ensuring better airflow and keeping your system cooler.
Cons:
1. Limited flexibility: Semi-modular PSUs are not as customizable as fully modular ones, as some cables are permanently attached.
2. Cable management challenges: The fixed cables can add clutter to the case, and it can be challenging to manage and hide them, which can impact airflow and aesthetics.
3. Limited future compatibility: As technology advances and newer components require more power, the fixed cables may not be suitable or may require adapters, lowering the efficiency and overall performance.
What is a Non-Modular PSU?
A Non-Modular PSU is a type of PSU that comes with a fixed set of cables attached to the unit. This means that all the cables, including those that you may not need, cannot be removed or replaced.
Non-Modular PSUs are often less expensive than their Modular counterparts but provide less flexibility in cable management. They are still a reliable and popular choice for budget-conscious PC builders who prioritize affordability over customizability. However, it is worth noting that Non-Modular PSUs can be more cluttered inside the case due to extra cabling.
Pros:
1. Cost-effective: Non-modular PSUs are generally cheaper than their modular counterparts. This is because they come with a fixed set of cables attached to them, which reduces manufacturing costs.
2. Easy to install: Non-modular PSUs come with all the cables you need to power your system, so installation is a breeze. You don’t have to worry about attaching any additional cables or configuring any settings.
3. Reliable: Non-modular PSUs are known for their reliability. PSU cables are soldered directly onto the unit, ensuring a secure and consistent connection over time. This also reduces the risk of loose or misaligned connections, reducing the potential for electrical failures or malfunctions.
4. Simple: Non-modular PSUs are often simpler than modular ones, which means less can go wrong. There are fewer to configure, making them a good choice for beginners.
Cons:
1. Cable Management: Non-modular PSUs come with a fixed set of cables that might not be used entirely in your system. This means you may have to find a way to manage the excess cables, which could be difficult in smaller cases.
2. Poor Airflow: The extra cables that come with a non-modular PSU can block the airflow in the case, leading to increased temperatures and decreased overall system performance.
3. Non-Upgradable: With a non-modular PSU, you can’t add or remove cables as your system changes. This means that you’ll have to purchase a whole new PSU if you want to upgrade your system.
4. Aesthetics: Excess cables from a non-modular PSU can create an unsightly mess in your case, leading to a less attractive overall look.
Modular vs Non-Modular PSUs: What is The Right For Your Build?
When it comes to choosing between a modular or non-modular PSU, the decision is ultimately up to you. If you’re looking for maximum flexibility and customization options, then a modular PSU is likely your best choice. However, if cost or simplicity is your primary concern, then a non-modular option might be better suited to your needs. Ultimately, the right choice depends on your individual requirements and budget restrictions.
Before investing in any type of power supply, make sure you do your research so that you know what type of unit will work best for your PC build. Also consider other factors such as efficiency ratings, wattage capabilities, and safety features when making a selection so that you get the most out of your investment. With careful consideration, you can choose the perfect PSU for your system.
What To Look For in a Quality PSU
When selecting a quality PSU, there are several features to consider, including its 80 PLUS certification and required wattage. The 80 PLUS certification ensures that the power supply is energy efficient and minimizes power usage. Meanwhile, the required wattage should be determined by the components of the computer, with a higher wattage suggested for more powerful systems. Overall, investing in a high-quality PSU can improve system stability and reliability while reducing energy costs over time.
80 PLUS Certification: The Efficiency of The PSUs
The 80 PLUS program is an initiative established in 2004 to encourage energy efficiency in power supply units. Through this voluntary certification process, manufacturers can demonstrate their commitment and help reduce global electricity consumption.
The certification tests the efficiency of PSUs at varying workloads, ranging from 10% to 100% of their labeled capacity. When a PSU is certified by 80 PLUS, it means it’s highly efficient and can significantly reduce power consumption, therefore, saving users money on their electricity bills.
There are several levels of certification as per the table below:
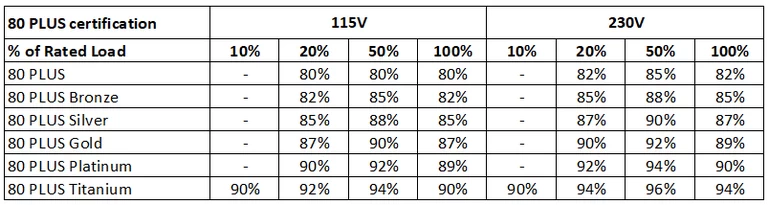
The higher the certification level, the more expensive the PSU will be. However, investing in a higher quality PSU can pay off in the long run by reducing electricity costs, providing better system stability, protecting your components from damage, and prolonging the lifespan of your system.
Required Wattage
Wattage ratings are also an essential factor to consider when purchasing a PSU. Wattage ratings refer to the maximum amount of power that a PSU can provide to your components. This number should be greater than the total power requirements of your system. If you have a high-end system with multiple graphics cards and high-wattage components, you will need a higher-wattage PSU. However, if you have a basic system with low-wattage components, you may not need as high of a wattage rating.
If you’re looking for a more precise estimation of the amount of wattage your system requires, just utilize online tools like EVGA Power Meter or the Outervision Power Supply Calculator. This interactive calculator enables you to input details about every part of your computer build and then it calculates how many total watts are needed for secure system functionality. Plus, this tool will also recommend extra components that can further optimize energy efficiency and minimize any wasted power usage.
There are multiple types of PSU connectors available that correspond with specific computer components. The most well-known connectors include the 24-pin motherboard cables which power the motherboard, or 4-pin (or 2×4-pin) CPU power cables, and the 6 or 8-pin PCI Express connector which powers the graphics card. The PSU also provides other cables such as SATA and Molex power connectors that power hard drives and other peripherals.
RELATED: Where Does PCIe Cables Go – A Guide To Powering Graphics Cards?
It’s important to note that the wattage rating on a PSU isn’t the only factor that affects its performance. The voltage stability, and build quality of the PSU also play a vital role in its performance. Therefore, it’s essential to research and read reviews on different PSU models to ensure you’re getting a high-quality model that meets your needs.
Final Thoughts
In conclusion, the battle of power supplies is a crucial aspect to consider when building or upgrading a computer system. The decision to choose between modular and non-modular power supplies is a personal preference that is influenced by various factors such as budget, aesthetics, and cable management. Non-modular power supplies offer a cost-effective solution with less clutter and are ideal for those who want a budget and simple computer build. However, they might result in cable management issues and limit the airflow.
Modular power supplies, on the other hand, provide users with a higher level of customization and flexibility in terms of cable management, which contributes to better air circulation resulting in cooler components. Although they are a bit more expensive, they are the perfect choice for enthusiasts who love to have aesthetically pleasing builds with no cable clutter.
When considering the right power supply for any computer build, the decision of choosing between modular and non-modular is dependent on individual preferences and requirements. Ultimately, the right power supply should cater to the specific needs of the user’s computer hardware and budget constraints.







