We get a lot of questions about PCIe cables every day, such as what are PCIe cables? Where does PCIe cable go? Or where to plug in PCIe cable?
PCIe cables are separate 8-pin power cables that run directly from the Power Supply Unit to the graphics cards. Other than an 8-pin PCIe cable, in some cases this connector may be 6-pin or 6+2-pin.
Simple words, PCIe cables are used to power high-performance graphics cards. These cables draw power directly from the Power Supply Unit (PSU), and the other end is plugged into the graphics cards’ connector.
High performance graphics cards consume the most power. So understanding how to power it using a PCIe cables is essential, especially when you want to upgrade or build your own PC.
Discrete graphics cards are the components having PCIe interface. A full-sized ×16 PCIe card may draw up to 75W from the PCIe slot. There are actually a lot of high performance graphics cards consuming more than 75W. Thus, manufacturers use optional connectors to add 75 W (6-pin) or 150W (8-pin) of +12V or combination to the PCIe card.
In this post, we will discuss the importance of a PCIe cables in the following topics:
- Power Supply Capability Of PCIe Slots
- Where Does The PCIe Cables Go
- Specifications Of Some High Performance GPUs
- How To Choose A PSU?
- Powering For Graphics Cards
Power Capability Of PCIe Slots
The number of pins in PCIe slots with different lanes will vary:
- PCIe x16 lanes: 82 pins
- PCIe x8 lanes: 49 pins
- PCIe x4 lane: 32 pins
- PCIe x1 lane: 18 pins
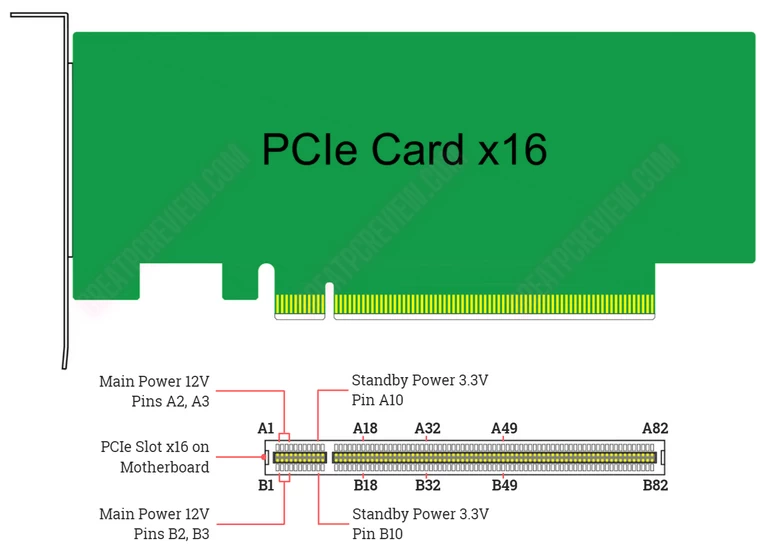
PCIe cards pull power from the motherboard through the power supply pins of the PCIe slot. The main 12V power supply for the PCIe slot is pins B2, B3 (side B) and pins A2, A3 (side A). Power standby 3.3V is pin B10 and A10. PCIe card x1 supplies up to 25W and x16 is 75W combined.
RELATED: Motherboard Components – A Guide To Building Your Own PC
Where Does The PCIe Cables Go
If you have a sound card or a network card, it will draw power from the motherboard only. However, for some graphics cards loads much power. It can be up to 400W or more. Thus, using PCIe cables to provide additional power supply from the PSU to the graphics cards is required. Optional connector for PCIe power cables could be:
- 6-pin x 1 for 75W, +12V or
- 8-pin x 1 for 150W, +12V or
- 6-pin x 2 + 8-pin x 1 for 300W, +12V or
- 8-pin x 2 for 300W, +12V
Many manufacturers even offer graphics cards with more power than specifications. For example, GeForce RTX™ 3090 SUPRIM X 24G, requires three PCIe power cables with connectors 8-pin for a total load of 420W.
If you’re a gamer, you probably want to boost your PC’s graphics power by using multi-GPU technology like NVIDIA’s SLI or AMD’s Crossfire. Building your own PC using such a high load of GPU, you need certain knowledge relating to PSU.
RELATED: What Is SLI? Is SLI Worth It? A Guide for Multi-GPU Technology
Specifications Of Some High Performance Graphics Cards
There are some well-known graphics cards on the market, such as ASUS, MSI, Gigabyte, EVGA. But, these graphics cards mainly use GPU chips from NVIDIA and AMD. Table below is the major specifications of some certain power-hungry graphics cards.
| Model Name | Manufacturer | GPU Chip | Power | PCIe Version x Lanes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GeForce RTX™ 3090 SUPRIM X 24G | MSI | NVIDIA® GeForce RTX™ 3090 | 420W(8-pin x 3) | PCIe 4.0 x16 |
| GeForce RTX™ 3080 Ti SUPRIM X 12G | MSI | NVIDIA® GeForce RTX™ 3080 Ti | 400W (8-pin x 3) | PCIe 4.0 x16 |
| EVGA GeForce RTX 3070 Ti FTW3 ULTRA GAMING | EVGA | NVIDIA® GeForce RTX™ 3070 | 320W (8-pin x 2) | PCIe 4.0 x16 |
| Radeon™ RX 6900 XT GAMING TRIO 16G | MSI | AMD Radeon™ RX 6900 XT | 300W (8-pin x 3) | PCIe 4.0 x16 |
| Radeon™ RX 6800 XT GAMING TRIO PLUS 16G | MSI | AMD Radeon™ RX 6800 XT | 300W (8-pin x 3) | PCIe 4.0 x16 |
| RX 6700 XT MECH 2X 12G | MSI | AMD Radeon™ RX 6700 XT | 230W (8-pin x 2) | PCIe 4.0 x16 |
How To Choose A PSU?
As stated at the outset of this article, the CPU and GPU are the biggest consumers on your PC. So the first thing when choosing a PSU is to calculate how much power your PC needs. And how much extra wattage to reserve for future PC upgrades. Also, you have to find out some other factors such as PSU size, modular, power rails, number of PCIe cables that are required and its efficiency.
RELATED: Modular Vs Non-Modular PSUs: The Battle Of Power Supplies
Wattage Calculation
Components on PCs draw power from the PSU. Motherboard, CPU, GPU, RAM, Storage devices, … all need enough power to operate as well. The power demand will also increase if you overclock the CPU or GPU.
We could find several tools online to calculate wattage. Outervision’s Power Supply Calculator (1) can be a good choice. This tool may calculate the total power required and also give us some recommendations. On Outervision’s calculator interface, there are two options, Basic and Expert. If you are not overclocking the CPU or GPU then you can use Basic calculation. In Expert mode, you can set up to 2 CPUs or GPUs and enter overclocking parameters for them.
As an example of power calculation shown in the picture below. The PC with Intel Core i7-9700F CPU, Nvidia Geforce GTX 1060 GPU. And some generic components, like 2x16GB DDR4 RAM, M2 NVMe SSD and a SATA HDD. As calculation results, the PC’s wattage is 289W. The calculator tool recommended PSU is 450W.

Of course, you can choose a PSU as the recommendation of such calculator tool. Further, you may select a PSU with a higher wattage, keeping in mind that the PSU’s efficiency is highest at 50% of the load. You should also include added power demand for future upgrades in this calculation.
PSU Form Factor
The most PSUs used for desktop PCs today are the ATX and SFX power supply. Size of ATX form factor is 150mm width, 86mm height, and 140mm depth. While SFX’s size is 125mm width, 63.5mm height, and 100mm depth.
SFX form factor may be used for small sized PC models. For example, in some PC’s cases with microATX motherboards, we could insert a PSU of ATX or SFX size.
TFX form factor is less used. As we apply this form factor for mini-ITX motherboards. Size of the TFX form factor is width x height x depth = 85mm x 64mm x 175mm.
Modular Cable Or Fixed Cable?
Modular power supply is an extra option in modern PSUs. As today, there are so many different types of graphics cards, the power demand on PCs is increasing every day. In conventional PSU, all cables are pre-soldered in one end. And of course, some of them may not be used. The presence of unused cables reduces the space inside the PC case. And it obstructs airflow within the computer.
With a modular PSU, you only insert the necessary power cables. This overcomes the disadvantages of PSUs with fixed power cables. Fully-modular PSU is the one having 100% detachable power cables. While in semi-modular PSU, there are some fixed cables such as ATX 24 pins, EPS 8-pins. And the remaining are detachable cables.
Unless you have to consider your budget. I would suggest going with the modular power supply. Further, the power socket available on the modular PSU should be capable of supplying all of the graphics card’s connectors.

Single-Rail Or Multiple-Rail?
Power rails are separate cable groups that provide a certain voltage. For example +3.3V rail, +5V rail, +12V rail. Each power rail has its own over current protection (OCP) threshold. As stipulated by Intel’ ATX power supply standard version 2.0, the power limit of a +12v rail is 240 VA. That means on each +12V rail, there will be an OCP trip at 20A. This will help protecting the PSU and PC from over current or short circuit incidents. PSUs according to this standard must have multiple-rail + 12V for all necessary components.
Actually high performance components like graphics card need a combination of multiple-rail +12V. Then you have to balance the load on multiple-rail. Thus many manufacturers tend to increase the OCP limit or combine all +12V cable into single rail. With single-rail PSU, load balancing is no longer an issue. All you need to concern is to select a PSU with enough wattage as calculated above.
Multiple-rail is safer for your PC. But, as explained by Corsair’s PSU expert, Jon Gerow (2), the chance of a short circuit on single-rail PSU is only 99.9%. So both, multiple-tail or single-rail are fine. What you need to pay attention to is its safety features. Your PSU must have the following protection circuits:
- Over Current Protection (OCP),
- Over Voltage Protection (OVP),
- Under Voltage Protection (UVP), and
- Short Circuit Protection (SCP).
80 PLUS Certification
PSU is a converter from wall AC (115V or 230V) to low voltage DC for PC operation. Like other electrical devices, the conversion will have a percentage of energy loss. Say, your PC’s power loads at 300W. The PSU pulls power from the wall AC is 400W. As a result, the PSU’s efficiency is 75% (300/400). Power loss on the PSU is 100W (25%). This loss actually is the heat inside the PSU.
Efficiency is an important feature of a PSU. A high-efficiency PSU will save your money and keep the PSU operation in quiet.
With 80 PLUS certification, the efficiency of the PSU will be 80% or more. 80 PLUS is available in different levels, ranging from Basic to Titanium as per the table below:
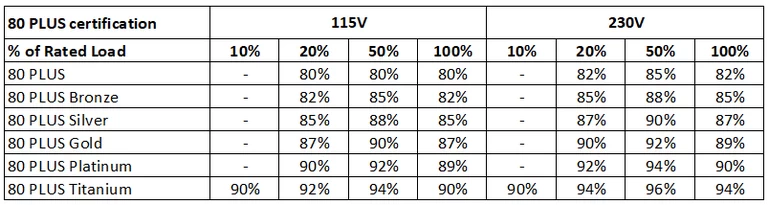
As shown in the table, highest efficiency of PSU always reaches at 50% of the load. For example you have a 700W PSU with 80 PLUS gold certification, input voltage at 115V. It reaches the highest efficiency of 90% when PC loading at 350W.
Powering For Graphics Card
Power sockets on graphics cards could be 6-pin or 8-pin types. So at the PCIe cables, there have corresponding types: 6 pin, 6+2 pin, or 8 pin connector.
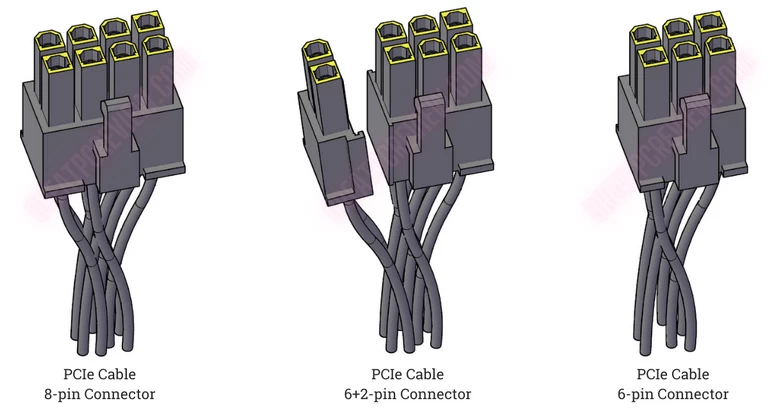
The power socket on the PSU side that supplies power to the graphics card is usually named as PCIe/CPU or VGA. And on the cable connector you may see a marking as “PCI-E”. If you buy more PCIe cables for the graphics card, it is best to get added cables from the same PSU’s manufacturer.
It is critical to note that regardless of which PSU you select, you must ensure that it provides a sufficient number of PCIe cables to connect to the graphics cards. Furthermore, the connector for the PCIe cables must be distinguished from the ATX12V/ESP12V connector for the CPU, as these two types of connectors are very similar (as shown below).

Graphics cards are a high performance component. Thus, the connecting of power cables must direct go from the PSU, without adapters or splitters.
Summary
Hopefully, this article has provided you with useful information about PCIe cables and related notes to consider when purchasing your PSU.
Power is the life-sustaining heart of your PC. Choosing a power supply for your computer with a high performance graphics card is a decision that requires careful research.
I recommend you choosing power supplies from reputable manufacturers and thoroughly reading their specifications before making a specific decision.












