As technology advances, there is an ever-growing demand for faster and more efficient components in our electronic devices. Random Access Memory, or RAM, plays a critical role in the performance of computer systems. It is responsible for temporary data storage necessary for immediate access by the computer’s operating system and applications.
So, what RAM should I buy? A quick way to determine this is to use an online tool combined with your computer’s manual. It is also important to factor in performance and budget when making your decision.
This blog post will explain the specific considerations you should keep in mind while selecting the suitable RAM for your system. By understanding all the aspects that go into purchasing memory upgrades for computers, you can ensure that you get the best possible product for your needs at an affordable cost.
Table of Contents
DDR Generations
RAM has evolved over the years, and different generations of RAM offer varying speeds, capacities, and compatibility with different computer systems. The distinction between RAM generations is mainly in their architecture, speed, and power usage.
The latest RAM generation, DDR5, provides faster data transfer rates than its predecessor. Older RAM generations, such as DDR2, DDR, and SDRAM, are now outdated and not commonly used in modern computer systems. Understanding the differences between RAM generations is crucial for maintaining and upgrading computer systems to get the best performance.
RELATED: Motherboard Components – A Guide To Building Your Own PC
What is DDR SDRAM?
DDR SDRAM, commonly known as Double Data Rate Synchronous Dynamic Random-Access Memory, is a type of RAM that facilitates faster data transfer between the memory and the processor. It is a newer generation RAM that emerged in the year 2000 and is the successor to SDRAM.
DDR can transmit data to the processor twice per cycle, which enables faster data transfer compared to its predecessor. Each subsequent generation of DDR has seen improvements in transfer rates, bandwidth, and voltage efficiency, providing higher overall system performance.
DDR3 vs. DDR4 vs. DDR5
There are different generations of DDR memory. DDR and DDR2 are the older generations and are now mostly obsolete. The most frequently utilized types of DDR memory at present are DDR3, DDR4, and DDR5.
DDR3 was first introduced in 2007 and continued to be widely used until DDR4 was introduced in 2014. DDR3 has a maximum transfer rate of 17 GB/s, a voltage of 1.5V, and typically comes in modules of 4 GB or 8 GB. DDR3 is compatible with older computers and is still used in some low-end systems today.
DDR4, on the other hand, has a maximum transfer rate of 25.6 GB/s and uses a lower voltage of 1.2V. DDR4 modules typically come in sizes of 8 GB or 16 GB. DDR4 is more power-efficient than DDR3 and offers faster performance, making it the most popular type of RAM used in modern computers.
DDR5 is the most recent generation of DDR RAM and promises even faster performance with a maximum transfer rate of 64 GB/s. It will also use a lower voltage than DDR4 and offer increased power efficiency. DDR5 is expected to become widely used in high-end systems for gaming, video editing, and other demanding applications.
Each generation of DDR RAM offers faster performance and improved power efficiency compared to the previous generation. DDR4 is currently the most popular and widely used, but DDR5 is on the horizon and promises even greater performance improvements.
What Type of RAM Is Compatible with Your PC?
When choosing a compatible RAM, it’s important to consider its form factor and generation. The form factor refers to the physical size and shape of the RAM, while generations determine compatibility and speed.
Form Factor
The form factor of RAM precisely determines the size and layout of the computer’s memory module. Among the RAM form factors available, the most common ones are DIMM and SO-DIMM.
The Dual In-line Memory Module (DIMM) is the standard RAM Form Factor for desktop computers and workstations. It is roughly 5.25 inches (133.35 mm) long. DIMM’s physical dimensions make it easy to install it in the motherboard’s memory slots.
On the other hand, the Small Outline Dual In-line Memory Module (SO-DIMM) is the standard RAM Form Factor for laptops and compact systems. The SO-DIMM is significantly smaller than the DIMM, measuring 2.67 inches (67.6 mm) long. The SO-DIMM’s smaller size enables it to fit inside the tighter spaces of portable systems.
DDR Generation Compatibility
DDR memory cannot be used interchangeably between different generations because it is not backward or forward-compatible. For instance, DDR3 memory cannot work in a motherboard designed for DDR4 memory. Conversely, DDR4 memory cannot work in a motherboard designed for DDR3 memory.
However, within the same generation, the RAM module is backward compatible. Meaning that faster memory sticks can be safely inserted into a motherboard designed to run slower memory. For example, a motherboard designed to run DDR3-1333 can support DDR3-1600 or even DDR3-1866, but these sticks will run at a slower speed of 1333MHz.
What RAM Should I Buy
Using online tools like Crucial System Advisor is a quick option to find the appropriate RAM module for your PC. However, the guide below will provide you with more options to choose from.
Looking for a RAM Module That is Compatible With Your System
When it comes to upgrading your computer’s memory or replacing a faulty module, it is essential to choose RAM that is compatible with your system. This involves considering the form factor and the DDR generation that your motherboard supports.
The form factor refers to the physical layout of the RAM sticks. DIMMs are larger and typically used in desktop systems, while SO-DIMMs are smaller and typically found in laptops and some small form factor desktops.
Each DDR generation has a different pin layout and key notch and they are not backward or forward-compatible. To find out which DDR generation your system supports, you can consult your motherboard or use diagnostic software such as CPU-Z. So before purchasing RAM, always ensure that it is compatible with your system’s specifications to avoid any potential issues.
How Much RAM Capacity Do I Need?
Determining the optimal amount of RAM capacity for your computer can be a challenging decision, especially when you consider the many factors that can influence performance. The amount of RAM you need ultimately depends on your intended use of the computer and the types of programs and applications that you plan to run.
In general, the more RAM you have, the better your computer’s performance will be. For most users, a minimum of 8GB of RAM is recommended, while power users and gamers may require 16GB or more. High-end video and photo editing applications also require significant amounts of RAM to function properly.
If you are purchasing a new computer, it’s important to consider future needs and potential upgrades. Choosing a computer with additional RAM slots can be a wise investment, as it allows you to increase the RAM capacity without having to replace the entire computer.
What RAM Speed Do I Need?
RAM speed for your system depends largely on the specific CPU and DDR generation you are working with. Generally speaking, higher RAM speeds can lead to improved overall system performance, particularly when used in conjunction with a modern CPU.
To illustrate this point, let’s consider the Intel Core i9-11900K processor and DDR4 RAM. This CPU supports DDR4-3200 memory, meaning that modules with a speed of up to 3,200 MT/s (25.600 MB/s) should be compatible with this processor. While it’s possible to use slower RAM modules with this CPU, choosing a higher speed can serve to unlock the true potential of your system.
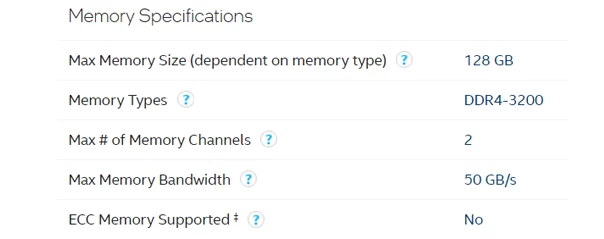
That being said, it’s important to remember that simply increasing RAM speed alone won’t always result in the best possible performance – other factors, such as storage speed and CPU thermals, can also play a role. To ensure you are making the right choice for your specific system, it’s crucial to do your research and consult with a knowledgeable specialist.
Dual-Channel RAM Configuration
Setting up a dual-channel RAM configuration in a computer system can significantly enhance its performance. Dual-channel RAM utilizes two identical memory modules that work together simultaneously to provide increased bandwidth and faster data access. Most DRAM manufacturers sell kits that include identical memory modules to enable users to set up a dual-channel configuration.
As an example, let us consider setting up dual-channel on the ASUS Prime Z590-A. This motherboard is built for the Intel LGA 1200 socket and supports DDR4 RAM up to 3200 MHz with Intel Core 11th Gen. processor. The motherboard has four memory slots, supporting up to a total of 128 GB of memory.
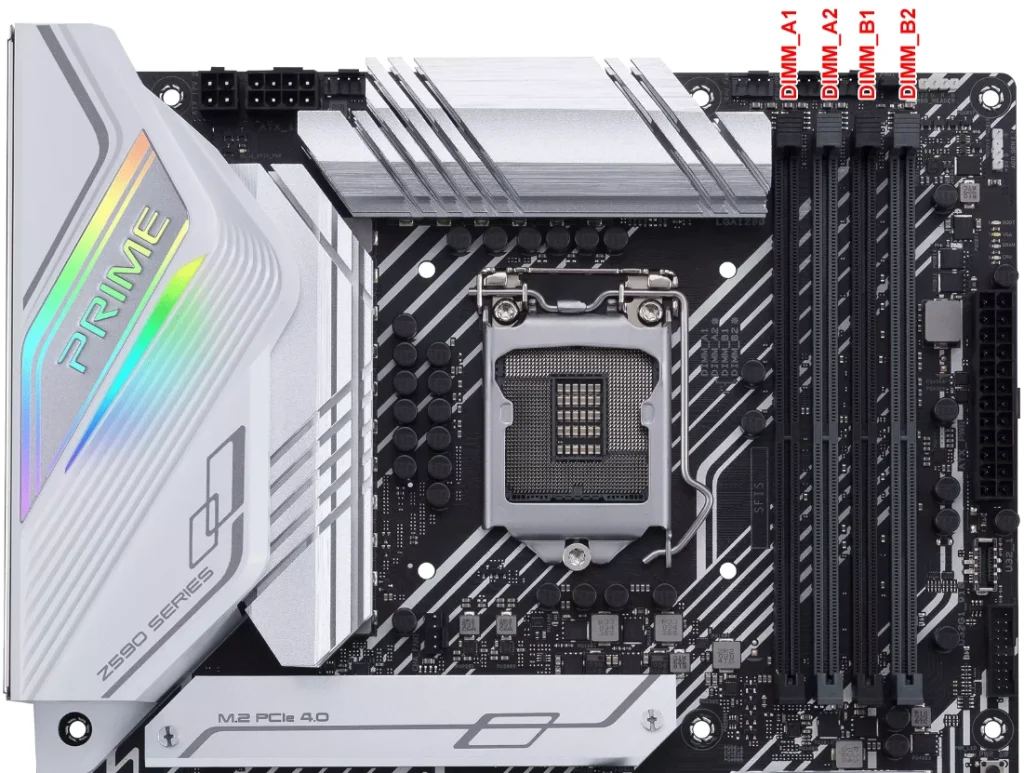

To enable dual-channel mode, install the memory modules in pairs into the same-colored slots. In this example, if you have two identical DDR4 memory modules, place them in the second and fourth memory slots (DIMM_A2 and DIMM_B2) for dual-channel operation.
RELATED: Which Slot To Put RAM In – A Guide To Optimal RAM Placement
CAS Latency
In addition to RAM speed, the CAS latency is also important as it can impact your system’s overall performance. CAS latency, also known as Column Access Strobe latency, is a timing parameter that determines how quickly the memory controller can access data stored in the memory modules. In simple terms, the lower the CAS latency, the quicker your computer will be able to access and transfer data.
When selecting RAM for your system, it’s important to look for a module that has the highest speed supported by both your processor and motherboard. The following consideration is to select the lowest possible CAS latency under your budget. This is because lower latency results in faster data transfer, but it comes at a higher cost. As a result, you should balance your budget to get the most out of your RAM modules.
Conclusion
Choosing the right RAM for your system can be a daunting task, but with some research and careful consideration of factors such as DDR generation, speed, and latency you can find an optimal match.
Dual-channel configurations are especially beneficial in terms of performance enhancement; however, it is also important to keep other components like storage drives and CPU thermals in mind when selecting memory modules.
When selecting RAM for your system take into account both its speed and CAS Latency rating to ensure that you get the best possible performance out of your computer.





